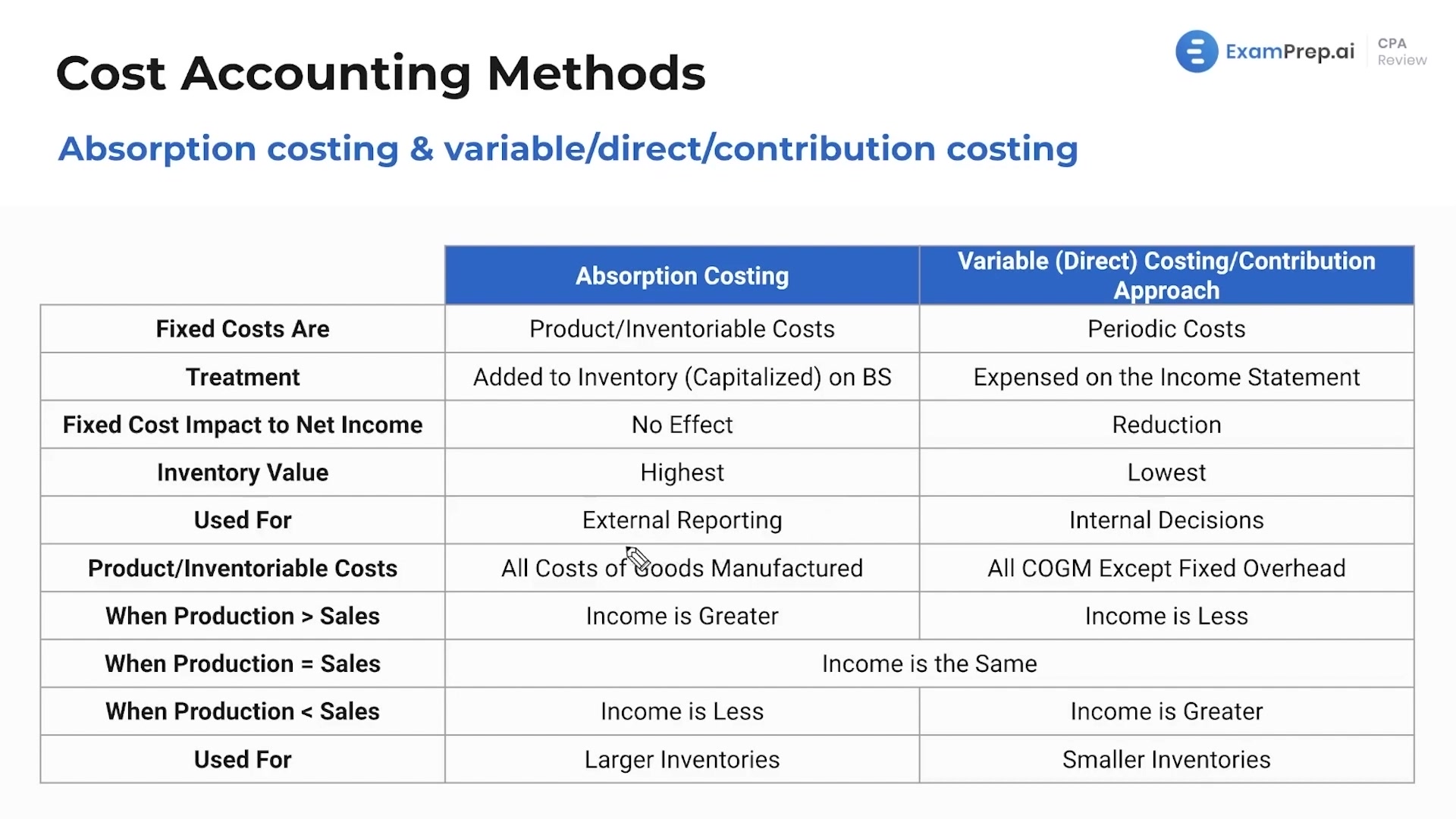
Absorption costing provides a more accurate, GAAP-compliant method of accounting for all production costs. By including fixed overhead costs in product costs, it presents a fuller, incremental view of profitability. The absorption costing method adheres to GAAP and provides an accurate, full-cost valuation of inventory. While more complex than variable costing, absorption costing gives managers and investors a clearer view of product profitability. Absorption costing leads to more accurate product costs than variable costing, which only includes direct costs.
Accounting Jobs of the Future: How Staffing Agencies Can Help Land Them
Instead of focusing on the overhead costs incurred by the product unit, these methods focus on assigning the fixed overhead costs to inventory. You can calculate a cost per unit by taking the total product costs / total units PRODUCED. Yes, you will calculate a fixed overhead cost per unit as well even though we know fixed costs do not change in total but they do change per unit. When we prepare the income statement, we will use the multi-step income statement format. Under absorption costing, the inventory carries a portion of fixed overhead costs in its valuation.
4: Comparing Absorption and Variable Costing
As a result, when using an absorption statement, it is common to find that the expense on the income statement is smaller. Variable cost Fixed MOH is a period cost and is treated as if it were ALL incurred regardless of the level of production. Both variables costing and abortion costing may produce different profits due to different inventories valuation techniques. These profits only differ in the presence of an opening and closing inventory.
- Further, the application of AC in the production of additional units eventually adds to the company’s bottom line in terms of profit since the additional units would not cost the company an additional fixed cost.
- It is to be noted that selling and administrative costs (both fixed and variable) are recurring and, as such, are expensed in the period they occurred.
- These extra units include the element of fixed cost because our absorption rate has both variable and fixed costs in it.
- replica watches uk
Managerial Accounting
It is anticipated that the units that were carried over will be sold in the next period. If the units are not sold, the costs will continue to be included in the costs of producing the units until they are sold. This treatment is based on the expense recognition principle, which is one of the cornerstones of accrual accounting and is why the absorption method follows GAAP. The principle states that expenses should be recognized in the period in which revenues are incurred. Including fixed overhead as a cost of the product ensures the fixed overhead is expensed (as part of cost of goods sold) when the sale is reported. Under generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP), absorption costing is required for external financial reporting.
In summary, absorption costing principles provide businesses with an accurate, GAAP-compliant accounting method to incrementally track product profitability changes tied to production volumes. By fully loading costs into inventory valuations, absorption costing standard costing system helps prevent distortions and presents a transparent view of operations. Overall, absorption costing adheres to GAAP principles for inventory valuation and provides a full allocation of all manufacturing costs to inventory and cost of goods sold.
Absorption Costing vs. Variable Costing: An Accounting Perspective
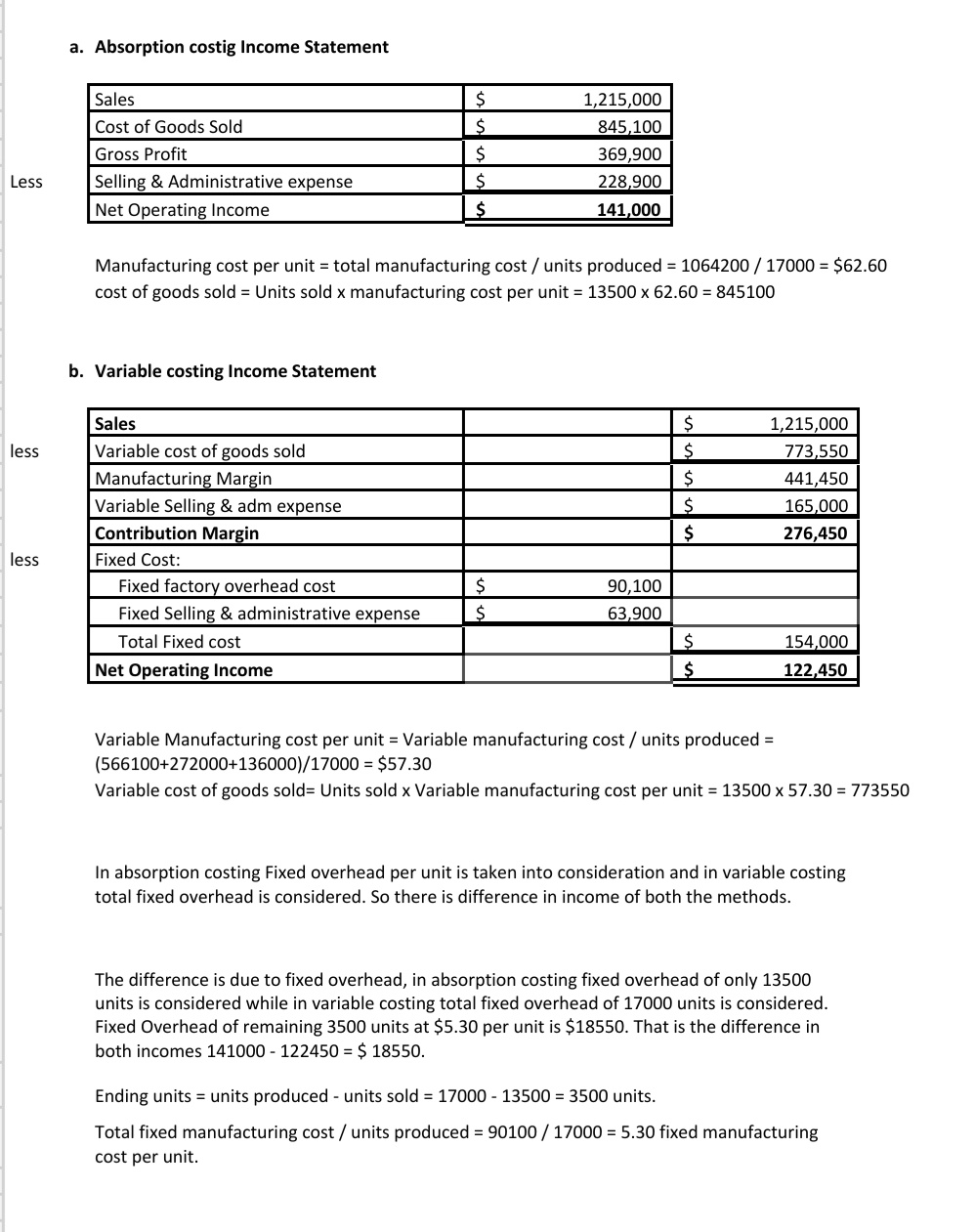
Fixed overhead costs can be calculated per unit because they change per unit and not in total. Because absorption costing includes fixed overhead costs in the cost of its products, it is unfavorable compared with variable costing when management is making internal incremental pricing decisions. This is because variable costing will only include the extra costs of producing the next incremental unit of a product. Carrying over inventories and overhead costs is reflected in the ending inventory balances at the end of the production period, which become the beginning inventory balances at the start of the next period.
This means that every cost must be included at the end of an inventory and is usually done as an asset on the balance sheet. As a result, it is not unusual to find out that there is a lower expense on the income statement when using an absorption statement. The income statement divides the period and product cost to have an overview of the costs. It shows that the gross profit is less than the selling and that the administrative expenses are equal to the operating income. The budgeted output was 150,000 units and the fixed costs of $300,000 are based on this budgeted output. But we can see that the manufactured units are 170,000, which means that 20,000 extra units have been produced.
This income statement looks at costs by dividing costs into product and period costs. In order to complete this statement correctly, make sure you understand product and period costs. Under generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP), U.S. companies may use absorption costing for external reporting, however variable costing is disallowed. The term absorption costing refers to the method in which the entire production cost is allocated to each and every output proportionately. It is a very common method used widely in the business especially in the manufacturing sector, and in this way the company is able to determine the cost of individual product and services. Since more costs are capitalized into inventory under absorption costing, the cost of goods sold recognized on the income statement tends to be lower in periods of rising production or increasing inventory levels.
The following diagram explains the cost flow forproduct and period costs. The following diagram explains the cost flow for product and period costs. The over-absorbed fixed costs need to be subtracted from the cost of sales. Calculate gross profit by subtracting the cost of goods sold from sales.
